Bar Chart
💡Example use cases:
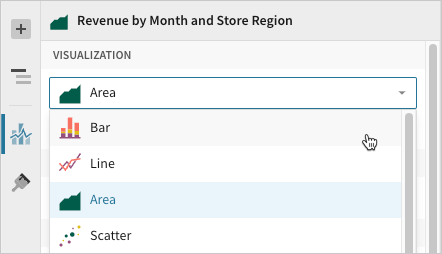
Basic bar chart requirements
🚩At the core of every chart is an underlying data table (derived from the data source) that supplies the information visualised by the chart. As you build a bar chart, Analytics Pro automatically calculates and structures the data to map the element properties to source columns in the underlying data table.
Add a bar chart
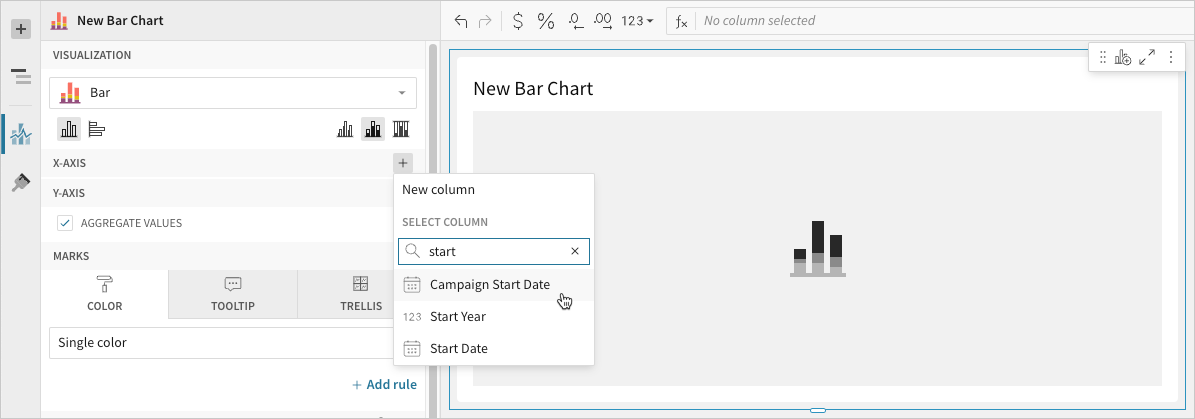
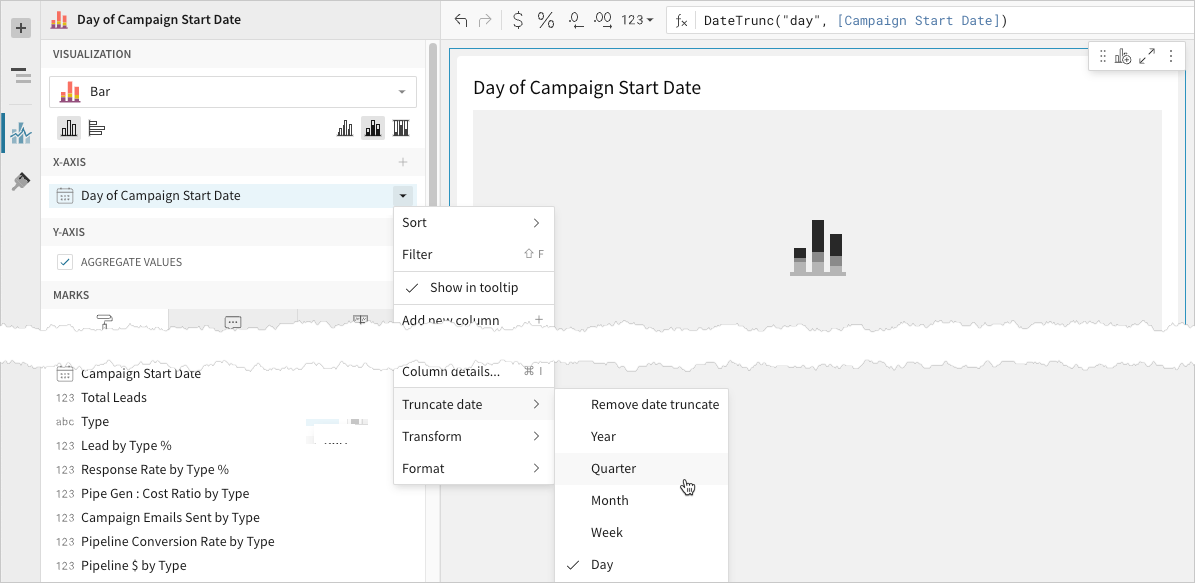
Define the categories
Define the variable
- 📘Bar charts support up to 25,000 data points. If the configurations result in a data set that exceeds this limit, the chart displays the first 25,000 data points, and a warning message indicates that the chart is incomplete. To reduce the number of data points, aggregate the values or apply data filters to the chart or source element.💡You can also select an existing column by dragging and dropping a column name from the Columns list to the applicable axis property.
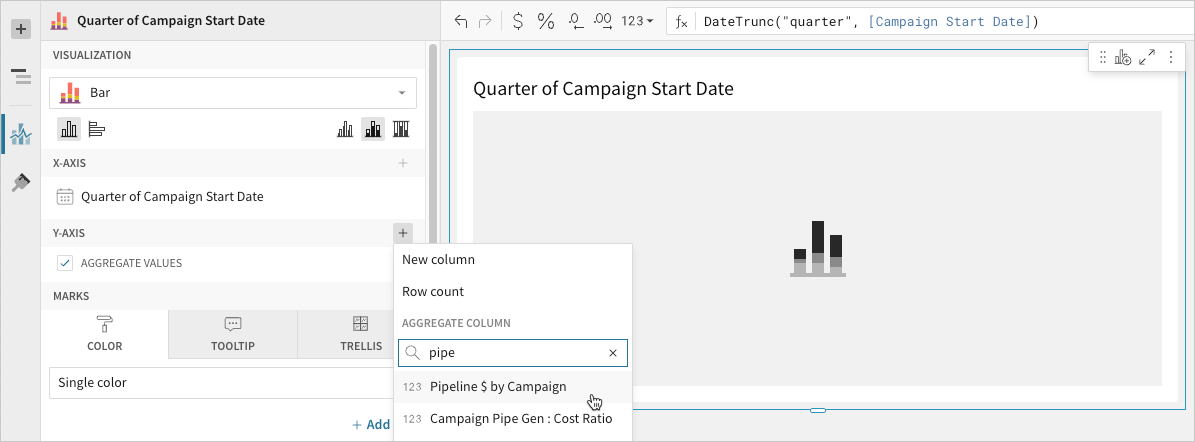
- 📘To plot the source column data without aggregating values, clear the Aggregate values checkbox in the Y-axis property. If this results in an incomplete chart that exceeds the 25,000 data point limit, reaggregate the values or apply data filters to reduce the number of data points.💡You can also use the toolbar to change the aggregation method (using the formula) and data label format.
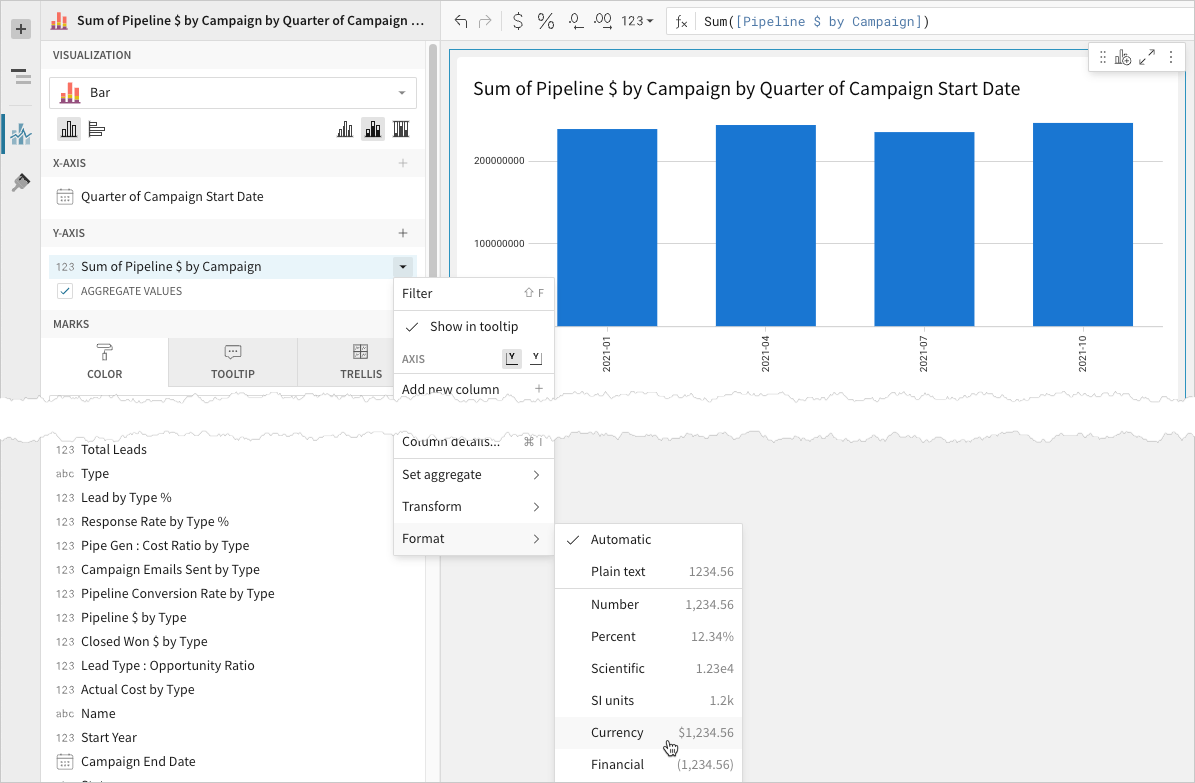
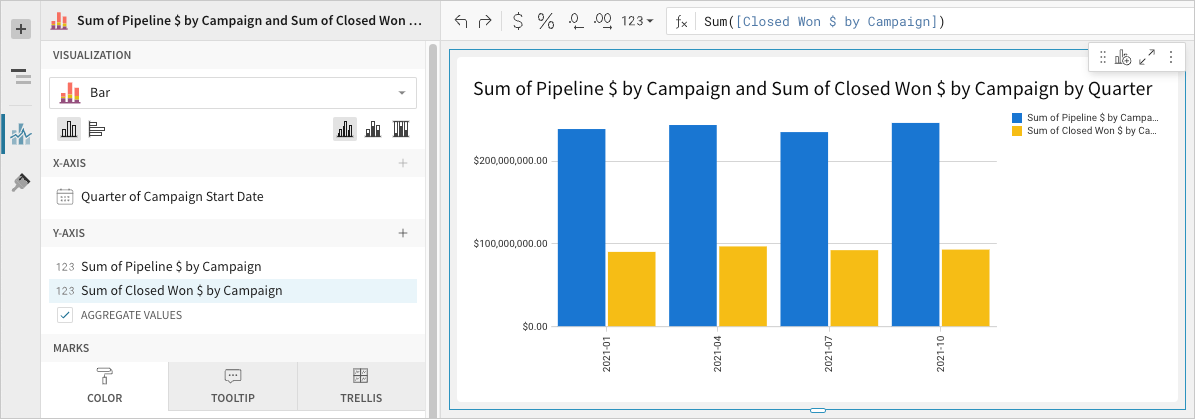
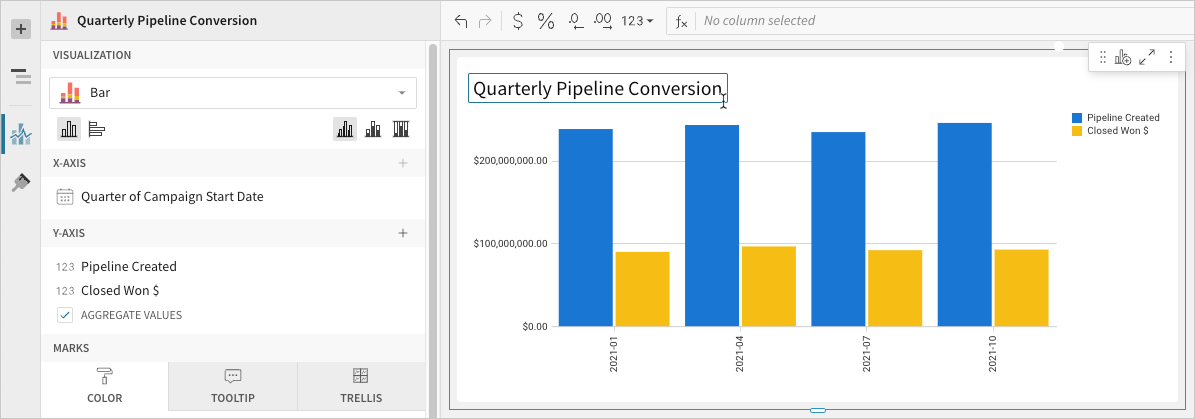
Advanced bar chart properties and formatting
Change orientation and stacking
Orientation
Stacking
Configure mark colours
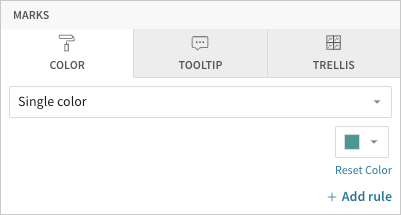
📘Multiple variables in the y-axis (in a vertical bar chart) or x-axis (in a horizontal bar chart) result in a stacked or clustered bar chart in which each data series represents a measure of a different variable. The By category colour setting can also generate bar stacks or clusters, but the resulting series represent sub-categories (within the configured chart categories) that measure the same variable.
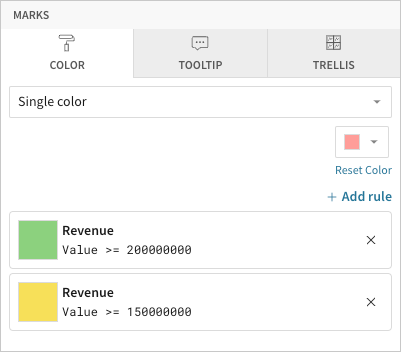
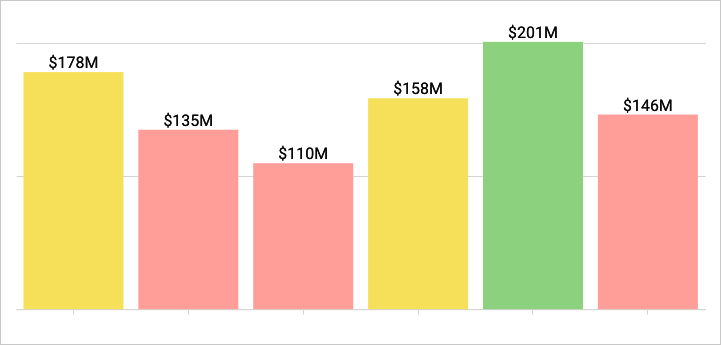
Add conditional formatting
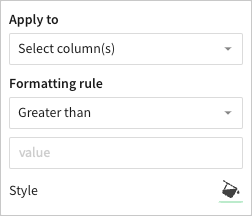
💡When the conditions of multiple rules are met, Analytics Pro applies the formatting rules in order of precedence, from top to bottom. Drag and drop rule blocks to reorder them as needed.
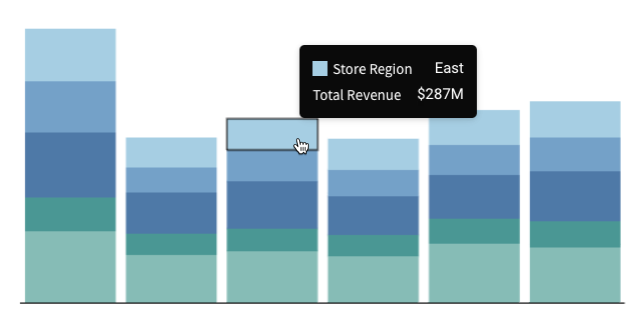
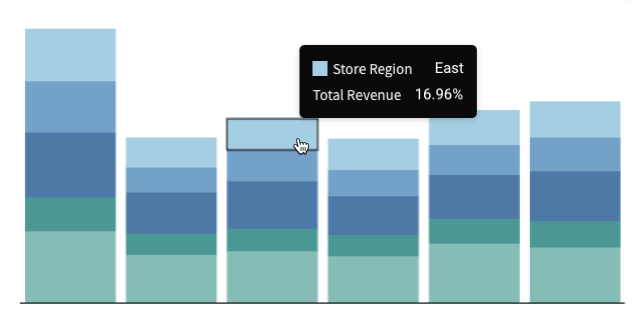
Customise tooltip fields and values
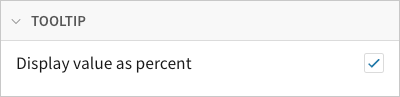
Tooltip value display
Resize gap width
Gap width
Last updated
Was this helpful?